Immigration Law Wiki
ELIGIBILITY FOR SIJS
General Eligibility Requirements for SIJ Classification
- Physically present in the United States at the time of filing and adjudication of the Petition for Amerasian, Widow(er), or Special Immigrant (Form I-360)
- Unmarried at the time of filing and adjudication of Form I-360
- Under the age of 21 at the time of filing Form I-360
- Subject to juvenile court determinations issued in the United States that meet the specified requirements
- Obtain U.S. Department of Homeland Security consent
- Obtain U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) consent, if applicable.
INA§101(a)(27)(J)
(codified at 8 U.S.C. § 1101(a)(27)(J)
(a) As used in this chapter— (1)–(26) * * * (27) The term “special immigrant” means—
(J) an immigrant who is present in the United States—
(i) who has been declared dependent on a juvenile court located in the United States or whom such a court has legally committed to, or placed under the custody of, an agency or department of a State, or an individual or entity appointed by a State or juvenile court located in the United States, and whose reunification with 1 or both of the immigrant’s parents is not viable due to abuse, neglect, abandonment, or a similar basis found under State law;
(ii) for whom it has been determined in administrative or judicial proceedings that it would not be in the alien’s best interest to be returned to the alien’s or parent’s previous country of nationality or country of last habitual residence;
and
(iii) in whose case the Secretary of Homeland Security consents to the grant of special immigrant juvenile status, except that—
(I) no juvenile court has jurisdiction to determine the custody status or placement of an alien in the custody of the Secretary of Health and Human Services unless the Secretary of Health and Human Services specifically consents to such jurisdiction; and
(II) no natural parent or prior adoptive parent of any alien provided special immigrant status under this subparagraph shall thereafter, by virtue of such parentage, be accorded any right, privilege, or status under this chapter;
PROCESS
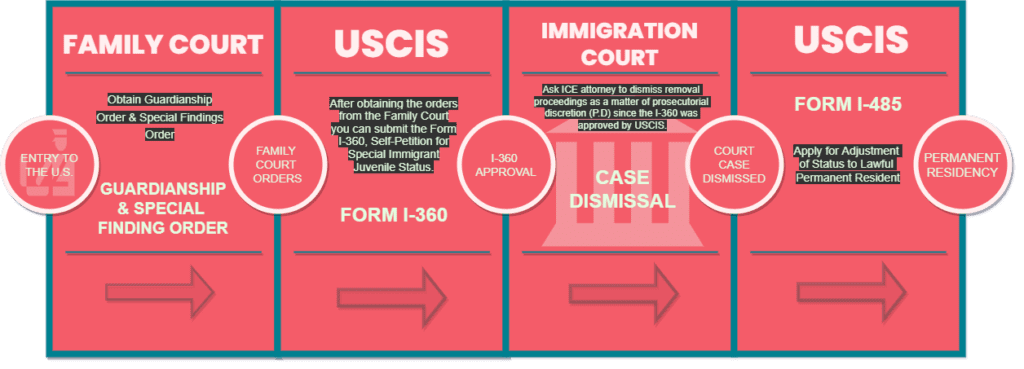
Age-out Protections for Filing with USCIS
In general, a juvenile may seek SIJ classification if he or she is under 21 years of age and unmarried at the time of filing the petition with USCIS. However, state law is controlling as to whether a petitioner is considered a “child” or any other equivalent term for a juvenile subject to the jurisdiction of a state juvenile court for custody or dependency proceedings.
If a petitioner was under 21 years of age on the date of the proper filing of the Form I-360, and all other eligibility requirements under the statute are met, USCIS cannot deny SIJ classification solely because the petitioner is older than 21 years of age at the time of adjudication.
USCIS RECENTLY IMPLEMENTED IN-PERSON APPOINTMENTS AT USCIS FIELD OFFICES FOR SIJS AGE-OUTS
For Applicants who are within a month of their 21st birthday, USCIS allows them to make an appointment to drop off their I-360 self-petition in-person to ensure it is timely filed.
Juvenile Court Order
For purposes of SIJ classification, a juvenile court is defined as a U.S. court having jurisdiction under state law to make judicial determinations on the dependency and/or custody and care of juveniles. This means the court must have the authority to make determinations about dependency and/or custody and care of the petitioner as a juvenile under state law at the time the order was issued. Depending on the circumstances, such a determination generally would be expected to remain in place until the juvenile reached the age of majority, or until the goal of a child welfare permanency plan, such as adoption, or other protective relief ordered by the juvenile court has been reached.
The title and the type of court that may meet the definition of a juvenile court varies from state to state. Examples of state courts that may meet this definition include: juvenile, family, dependency, orphans, guardianship, probate, and youthful offender courts.
Not all courts having jurisdiction over juveniles under state law may be acting as juvenile courts for the purposes of SIJ classification. For example, a court of general jurisdiction that issues an order with SIJ-related findings outside of any juvenile custody or dependency proceeding would generally not be acting as a juvenile court for SIJ purposes. The burden is on the petitioner to establish that the court is acting as a juvenile court at the time that the order is issued.
To be eligible for SIJ classification, the petitioner must submit a juvenile court order(s) with the following determinations, and the record must provide evidence that there is a reasonable factual basis for each of the determinations:
- Dependency or Custody – Declares the petitioner dependent on the court, or legally commits or places the petitioner under the custody of either a state agency or department, or a person or entity appointed by a state or juvenile court;
- Parental Reunification – Declares, under state law, that the petitioner cannot reunify with one or both of the petitioner’s parents due to abuse, neglect, abandonment, or a similar basis under state law; and
- Best Interests – Determines that it would not be in the petitioner’s best interest to be returned to the petitioner’s, or the petitioner’s parents’, country of nationality or last habitual residence. The best interest determination may be made by the juvenile court or in administrative proceedings authorized or recognized by the juvenile court.
